
We can easily find Zin from what we know already of the behavior of the transistor. This is simply the derivative of Vin with respect to Iin. In circuits with nonlinear elements such as a transistor, the input impedance of the transistor is defined as the reciprocal of the slope of the I versus V graph. In linear circuits (with resistors, capacitors, inductors, batteries, etc.) this ratio is the reciprocal of the slope of the I versus V graph. The most common examples are transimpedance gain and transadmittance gain. If the input and output quantities are different, the gain is no longer unitless. |A| less than unity indicates that the output is smaller than the input.

Negative gain is not possible for Power Gain. Note that a negative gain means that the sign of the signal is inverted. So far we have not specified the output quantity, the reason is that we can define the gain with respect to any given output and input quantity. Thus gain is defined as the ratio of the change in output to the change in input. For systems where the quiescent output is zero, this reduces to the ratio of the output to the input. Because transistor amplifiers often have a quiescent output (a non zero output when the input is zero) we define gain as the derivative of the output with respect to the input. Gain is defined as the ratio of the output signal to the input signal. This is the origin of the nomenclature of the three types of transistor amplifiers: common collector, common emitter, and common base.ĭefinition of Gain. The transistor is a three terminal device, thus the input and the output must share one terminal in common. From this perspective you can identify the base and the type of transistor based on the following equivalent circuits. (Why is that?) Most ohmmeters not only measure resistance, but also measure the forward voltage drop across a diode. Clearly a transistor cannot be made on the bench by combining two diodes. For a pnp transistor, VB must be at least 0.6 V less than VE otherwise, it will not pass collector-to-emitter current.īJT Schematic Symbols (Mnemonics for remembering the direction of the arrows are in parenthesis.) In terms of operation, this means that the base voltage VB of an npn transistor must be at least 0.6 V greater that the emitter voltage VE otherwise, the transistor will not pass emitter-to-collector current. For a pnp transistor, there is also a 0.6 V rise from the base to the emitter. For the npn transistor, there is a voltage drop from the base to the emitter of 0.6 V. For pnp transistors, the emitter voltage must be greater than the collector voltage by a similar amount. Rules for Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs): For an npn transistor, the voltage at the collector VC must be greater than the voltage at the emitter VE by at least a few tenths of a volt otherwise, current will not flow through the collector-emitter junction, no matter what the applied voltage at the base. It is desirable to operate transistor switches in or near the saturation region when in their on state. The collector current is strongly dependent on VCE unlike in the active region. The collector current varies very little with a change in the base current in the saturation region.

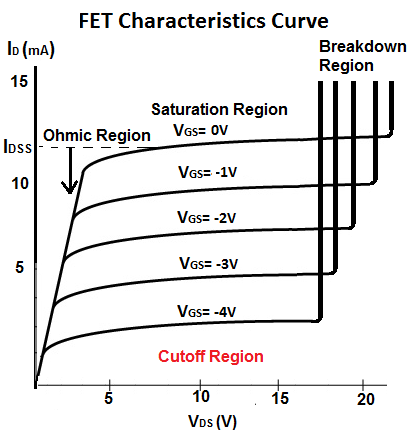
In this region the transistor can be an amplifier. The collector current is proportional to and controlled by the base current (IC = βIB) and relatively insensitive to VCE. (IB = 0 therefore IC = 0) Active region: The transistor is on. There is no conduction between the collector and the emitter. Regions of BJT operation: Cut-off region: The transistor is off. The gate-source voltage (VGS) controls the drain current (ID). In simple terms, it is a voltage controlled valve. The Field Effect Transistor (FET) is an active device. The base current (IB) controls the collector current (IC). In simple terms, it is a current controlled valve. The name transistor comes from the phrase “transferring an electrical signal across a resistor.” In this course we will discuss two types of transistors: The Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) is an active device. Lecture Notes on BJT & FET Transitors v1.1.1


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
